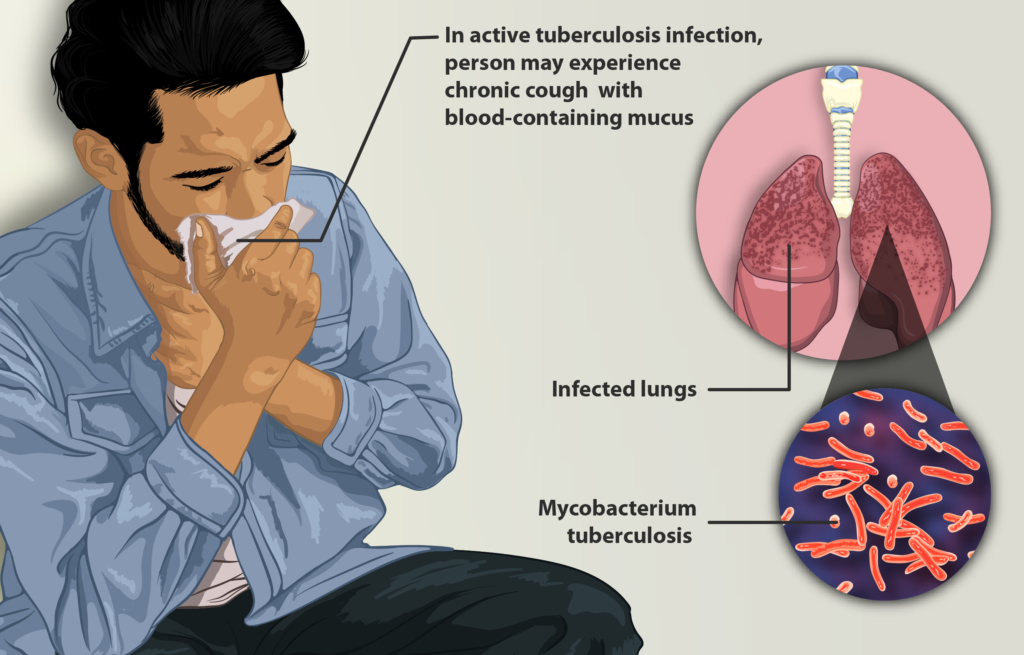
Tuberculosis (TB) is a serious infectious disease that affects millions of people worldwide. It is caused by a bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis and is primarily spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes or speaks. TB can cause a range of symptoms, including coughing, fever, fatigue, weight loss, and night sweats. While TB is a curable disease, if left untreated, it can be deadly. In this article, we will explore how TB can kill you.
If you or someone you know is at risk of dying from TB, it’s important to seek the help of a specialist. Dr. Rajeev Narang is the best TB specialist in Jaipur and can help you recover from this situation. With his expertise and guidance, you can receive the necessary treatment and care to improve your chances of recovery. Don’t wait – contact Dr. Rajeev Narang today and take the first step towards a healthier future.
What is TB?
TB is an infectious disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis bacteria. It primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body, such as the brain, spine, and kidneys. TB is spread through the air when an infected person coughs, sneezes, or talks, and another person inhales the bacteria. Once the bacteria are inhaled, they can travel to the lungs, where they can cause infection.
Food and Drinking Habits that Increase the Risk of TB
Certainly! In addition to the factors mentioned earlier, certain food and drinking habits can also increase the risk of developing TB. A diet lacking in essential nutrients such as vitamins A, C, and E, as well as minerals such as zinc, can weaken the immune system and make individuals more vulnerable to TB. Additionally, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can also weaken the immune system and increase the risk of developing TB. By maintaining a healthy diet and avoiding harmful habits, individuals can reduce their risk of developing TB and improve their overall health.
How TB Affects the Body
When the bacteria reach the lungs, they can cause a range of symptoms, including coughing, chest pain, and difficulty breathing. TB can also spread to other parts of the body, such as the brain, spine, and kidneys, through the bloodstream or lymphatic system. When TB affects other parts of the body, it can cause a range of symptoms depending on which part of the body is affected.
How TB Can Lead to Death
TB can be deadly in two ways: directly and indirectly. Direct death occurs when the bacteria cause complications in the lungs, such as pneumonia or respiratory failure. Indirect death occurs when TB weakens the immune system, making the person more susceptible to other infections and illnesses.
When TB causes pneumonia, it can fill the lungs with fluid, making it difficult for the person to breathe. This can lead to respiratory failure, which can be fatal if not treated quickly. If TB spreads to other parts of the body, it can cause a range of complications, such as meningitis, which can also be deadly.
When TB weakens the immune system, it can make the person more susceptible to other infections and illnesses. This can lead to a range of complications, including pneumonia, which can be fatal in some cases.
Who is at Risk of Dying from TB?
While anyone can develop TB, some people are at a higher risk of dying from the disease than others. People with weakened immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, are more vulnerable to TB-related mortality. Additionally, people living in poverty or with poor living conditions, such as those in crowded areas, are more likely to develop TB and experience severe complications.
Prevention and Treatment of TB
Prevention is key to stopping the spread of TB. This can be done through vaccination, good hygiene practices, and identifying and treating people with TB. TB is curable with antibiotics and drug-resistant TB treatment, but it is important to start treatment as soon as possible. Early detection and treatment can prevent complications and reduce the risk of death.
Conclusion
Tuberculosis is a serious infectious disease that can be deadly if left untreated. While TB can affect anyone, some people are at a higher risk of developing severe complications and dying from the disease. Prevention and early detection and treatment are crucial in stopping the spread of TB and reducing TB-related mortality. By understanding how TB can be deadly, we can work towards improving TB prevention and treatment and saving lives.